Python API¶
This section includes information for using the pure Python API of bob.ip.gabor.
List of Classes and Functions¶
| bob.ip.gabor.Wavelet | A class that represents a Gabor wavelet in frequency domain |
| bob.ip.gabor.Transform | A class that represents a family of Gabor wavelets that can be used to |
| bob.ip.gabor.Jet | A Gabor jet contains the responses of all Gabor wavelets of the Gabor |
| bob.ip.gabor.Similarity | A class that computes different kind of similarity function, i.a., disparity corrected Gabor phase differences. |
| bob.ip.gabor.Graph | A class to extract Gabor jets from a Gabor transformed image (see |
| bob.ip.gabor.load_jets((hdf5) -> jets) | Loads a list of Gabor jets from the given HDF5 file, which needs to be open for reading. |
| bob.ip.gabor.save_jets((jets, hdf5) -> None) | Saves the given list of Gabor jets to the given HDF5 file, which needs to be open for writing. |
Detailed Information¶
- class bob.ip.gabor.Graph¶
Bases: object
A class to extract Gabor jets from a Gabor transformed image (see bob.ip.gabor.Transform.transform())
The graph structure stores a list of nodes, where Gabor jets will be extracted from the images. These nodes are stored with absolute positions, so please assure that the image is large enough.
Constructor Documentation:
- bob.ip.gabor.Graph (righteye, lefteye, between, along, above, below)
- bob.ip.gabor.Graph (first, last, step)
- bob.ip.gabor.Graph (nodes)
- bob.ip.gabor.Graph (hdf5)
Creates a the Gabor graph
There are three different ways to create a Gabor graph. The first two ways will generate nodes in regular grid positions, while the third can specify the positions as a list of tuples.
Parameters:
righteye, lefteye : (int, int)
The position of the left and the right eye of the face in the image; the positions are with respect to the person in the image, so normally lefteye[1] > righteye[0]between : int
The number of nodes that should be placed between the eyes (excluding both eye nosed)along : int
The number of nodes that should be placed to the left of the right eye and to the right of the left eye (excluding the eye positions)above : int
The number of nodes that should be placed above the eyes (excluding the eye positions)below : int
The number of nodes that should be placed below the eyes (excluding the eye positions)first : (int, int)
The position of the first (top-left) node that will be placedlast : (int, int)
The position of the last (bottom-right) node that will be placed; depending on the step parameter, the actual bottom-right node might be before laststep : (int, int)
The distance between two each nodes (in vertical and horizontal direction)nodes : [(int, int)]
The node positions that should be stored in the graphhdf5 : bob.io.base.HD5Ffile
An HDF5 file open for reading to load the nodes of the Gabor graph fromClass Members:
- extract()¶
- extract(trafo_image, jets) -> None
- extract(trafo_image) -> jets
This function extracts all Gabor jets from the given trafo image for all nodes of the graph
The trafo image should have been created by a call to bob.ip.gabor.Transform.transform(). It must be assured that all nodes of the graph are inside the image boundaries of the trafo image.
Note
The function __call__() is a synonym for this function.
Parameters:
trafo_image : array_like (complex, 3D)
The Gabor wavelet transformed image, e.g., the result of bob.ip.gabor.Transform.transform()jets : [bob.ip.gabor.Jet]
The list of Gabor jets that will be filled during the extraction process; The number of jets must be identical to number_of_nodes, and the jets must have the correct bob.ip.gabor.Jet.length.Returns:
jets : array_like (complex, 3D)
The transformed image in spatial domain that will contain the transformed image; will have shape (number_of_wavelets, input.shape[0], input.shape[1])
- load(hdf5) → None¶
Loads the list of node positions of the Gabor graph from the given HDF5 file
Parameters:
hdf5 : bob.io.base.HDF5File
An HDF5 file opened for reading
- nodes¶
[(int, int)] <– The list of node positions extracted by this graph
Warning
You can use this variable to reset the nodes in this graph, but only by using the = operator. Something like graph.nodes[0] = (1,1) will not have the expected outcome!
- number_of_nodes¶
int <– The number of nodes that this Graph will extract
- save(hdf5) → None¶
Saves the the list of node positions of the Gabor graph to the given HDF5 file
Parameters:
hdf5 : bob.io.base.HDF5File
An HDF5 file open for writing
- class bob.ip.gabor.Jet¶
Bases: object
A Gabor jet contains the responses of all Gabor wavelets of the Gabor wavelet family at a certain position in the image
The Gabor jet represents the local texture at a certain offset point of an image that it was extracted from. Commonly, the complex-valued Gabor jet is stored as a vector of absolute values and a vector of phase values. Also, usually the Gabor jet is normalized to unit Euclidean length.
Constructor Documentation:
- bob.ip.gabor.Jet ([length])
- bob.ip.gabor.Jet (trafo_image, position, [normalize])
- bob.ip.gabor.Jet (complex, [normalize])
- bob.ip.gabor.Jet (to_average, [normalize])
- bob.ip.gabor.Jet (hdf5)
Creates a Gabor jet from various sources of data
The family of Gabor wavelets
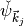 is
created by considering several center frequencies
is
created by considering several center frequencies 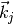 :
: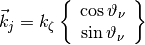
where
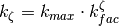 with
with
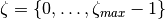 and
and
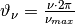 and
and
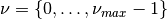
Parameters:
length : int
[default: 0] Creates an empty Gabor jet of the given lengthtrafo_image : array_like(complex, 3D)
The result of the Gabor wavelet transform, i.e., of bob.ip.gabor.Transform.transform()position : (int, int)
The position, where the Gabor jet should be extractedcomplex : array_like(complex, 3D)
The complex-valued representation of a Gabor jetto_average : [bob.ip.gabor.Jet]
Computes the average of the given Gabor jets, see average() for detailsnormalize : bool
[default: True] Should the newly generated Gabor jet be normalized to unit Euclidean length?hdf5 : bob.io.base.HD5Ffile
An HDF5 file open for reading to load the Gabor jet fromClass Members:
- abs¶
array(float,1D) <– The list of absolute values of the Gabor jet
- complex¶
array(complex,1D) <– The complex representation of the Gabor jet
Note
The complex representation is generated on the fly and is not stored anywhere in the object.
- extract(trafo_image, position[, normalize]) → None¶
Initializes the Gabor jet with the given complex-valued data extracted from the given trafo image at the given position
Parameters:
trafo_image : array_like(complex, 3D)
The result of the Gabor wavelet transform, i.e., of bob.ip.gabor.Transform.transform()position : (int, int)
The position, where the Gabor jet should be extractednormalize : bool
[default: True] Should the newly generated Gabor jet be normalized to unit Euclidean length?
- init(complex[, normalize]) → None¶
Initializes the Gabor jet with the given complex-valued data
Parameters:
complex : array_like(complex,1D)
The vector of complex data to initialize the Gabor jet withnormalize : bool
[default: True] Should the newly generated Gabor jet be normalized to unit Euclidean length?
- jet¶
array(float,2D) <– The absolute and phase values of the Gabor jet
The absolute values are stored in the first row jet[0,:], while the phase values are stored in the second row jet[1,:]
- length¶
int <– The number of elements in the Gabor jet
- load(hdf5) → None¶
Loads the Gabor jet from the given HDF5 file
Parameters:
hdf5 : bob.io.base.HDF5File
An HDF5 file opened for reading
- normalize() → old_norm¶
Normalizes the Gabor jet to unit Euclidean length and returns its old length
Note
Only the absolute values abs are affected by the normalization
Returns:
old_norm : float
The Euclidean length of the Gabor jet before normalization
- phase¶
array(float,1D) <– The list of phase values of the Gabor jet
- save(hdf5) → None¶
Saves the Gabor jet to the given HDF5 file
Parameters:
hdf5 : bob.io.base.HDF5File
An HDF5 file open for writing
- class bob.ip.gabor.Similarity¶
Bases: object
A class that computes different kind of similarity function, i.a., disparity corrected Gabor phase differences.
The implementation is according to [Guenther2011] and [Guenther2012], where all similarity functions are explained in more details.
Constructor Documentation:
- bob.ip.gabor.Similarity (type, [transform])
- bob.ip.gabor.Similarity (hdf5)
Creates a Gabor wavelet similarity function of the given type
Currently, several types of Gabor jet similarity functions are implemented. Please refer to [Guenther2012] for details.
Parameters:
type : str
The type of the Gabor jet similarity function; might be one of ('ScalarProduct', 'Canberra', 'Disparity', 'PhaseDiff', 'PhaseDiffPlusCanberra')transform : bob.ip.gabor.Transform
The Gabor wavelet transform class that was used to generate the Gabor jets; only required for disparity-based similarity functions (‘Disparity’, ‘PhaseDiff’, ‘PhaseDiffPlusCanberra’)hdf5 : bob.io.base.HD5Ffile
An HDF5 file open for reading to load the parametrization of the Gabor wavelet similarity fromClass Members:
- disparity(jet1, jet2) → disparity¶
This function computes the disparity vector for the given Gabor jets
This function is only available for convenience, it does not need to be called before similarity() is called.
Parameters:
jet1, jet2 : bob.ip.gabor.Jet
The two Gabor jets to compute the disparity betweenReturns:
disparity : (float, float)
The disparity vector estimated from the given Gabor jets
- last_disparity¶
(float, float) <– The disparity that was computed during the last call to similarity() or disparity().
- load(hdf5) → None¶
Loads the parametrization of the Gabor jet similarity from the given HDF5 file
Parameters:
hdf5 : bob.io.base.HDF5File
An HDF5 file opened for reading
- save(hdf5) → None¶
Saves the parametrization of this Gabor jet similarity to the given HDF5 file
Parameters:
hdf5 : bob.io.base.HDF5File
An HDF5 file open for writing
- similarity(jet1, jet2) → sim¶
This function computes the similarity between the two given Gabor jets
Depending on the type, different kinds of similarities are computed (see [Guenther2011] for details). Some of them will also compute the disparity from the first to the second Gabor jet, which can be retrieved by last_disparity.
Note
The function __call__() is a synonym for this function.
Parameters:
jet1, jet2 : bob.ip.gabor.Jet
The two Gabor jets that should be comparedReturns:
sim : float
The similarity between the two Gabor jets; more similar Gabor jets will get higher similarity values
- transform¶
bob.ip.gabor.Transform or None <– The Gabor wavelet transform used in the similarity class; can be None for similarity functions that do not compute disparities
- type¶
str <– The type of the Gabor jet similarity function
- class bob.ip.gabor.Transform¶
Bases: object
A class that represents a family of Gabor wavelets that can be used to perform a Gabor wavelet transform
The implementation is according to [Guenther2011], where the whole procedure is explained in more detail.
Note
In opposition to the Wavelet class, here all input and output images are considered to be in spatial domain.
Constructor Documentation:
- bob.ip.gabor.Transform ([number_of_scales], [number_of_directions], [sigma], [k_max], [k_fac], [power_of_k], [dc_free], [epsilon])
- bob.ip.gabor.Transform (hdf5)
Creates a Gabor wavelet transform for the given parametrization
The family of Gabor wavelets
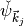 is
created by considering several center frequencies
is
created by considering several center frequencies 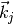 :
: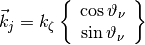
where
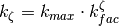 with
with
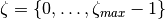 and
and
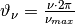 and
and
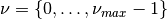
Parameters:
number_of_scales : int
[default: 5] The number of scales of Gabor
wavelets that should be created
of Gabor
wavelets that should be creatednumber_of_directions : int
[default: 8] The number of directions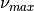 of
Gabor wavelets that should be created
of
Gabor wavelets that should be createdsigma : float
[default: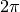 ] The spatial resolution
] The spatial resolution 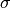 of the Gabor wavelets
of the Gabor waveletsk_max : float
[default: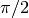 ] The highest frequency (the lowest
scale) of Gabor wavelets; the default will resemble to the
smallest wavelength of 4 pixels
] The highest frequency (the lowest
scale) of Gabor wavelets; the default will resemble to the
smallest wavelength of 4 pixelsk_fac : float
[default: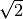 ] The (logarithmic) distance between
two scales of Gabor wavelets
] The (logarithmic) distance between
two scales of Gabor waveletspower_of_k : float
[default: 0] The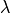 factor to regularize the Gabor
wavelet prefactor to generate comparable results for images,
see Appendix C of [Guenther2011]
factor to regularize the Gabor
wavelet prefactor to generate comparable results for images,
see Appendix C of [Guenther2011]dc_free : bool
[default: True] Should the Gabor wavelet be without DC factor (i.e. should the integral under the wavelet in spatial domain vanish)?epsilon : float
[default: 1e-10] For speed reasons: all wavelet pixels in frequency domain with an absolute value below this should be considered as 0hdf5 : bob.io.base.HD5Ffile
An HDF5 file open for reading to load the parametrization of the Gabor wavelet transform fromClass Members:
- dc_free¶
bool <– Are the Gabor wavelets DC free?
- generate_wavelets(height, width) → None¶
This function generates the Gabor wavelets for the given image resolution
This function is only available for convenience, it does not need to be called before transform() is called.
Parameters:
height : int
The height of the image to generate the wavelets forwidth : int
The width of the image to generate the wavelets for
- k_fac¶
float <– The logarithmic distance between two levels of Gabor wavelets
- k_max¶
float <– The highest frequency of Gabor wavelets
- load(hdf5) → None¶
Loads the parametrization of the Gabor wavelet transform from the given HDF5 file
Parameters:
hdf5 : bob.io.base.HDF5File
An HDF5 file opened for reading
- number_of_directions¶
int <– The number of directions (orientations) of Gabor wavelets
- number_of_scales¶
int <– The number of scales (levels) of Gabor wavelets
- number_of_wavelets¶
int <– The number of Gabor wavelets (i.e, the number of directions times the number of scales) of this class
- power_of_k¶
float <– The adaptation of the Gabor wavelet scales to get homogeneous values
- save(hdf5) → None¶
Saves the parametrization of this Gabor wavelet transform to the given HDF5 file
Parameters:
hdf5 : bob.io.base.HDF5File
An HDF5 file open for writing
- sigma¶
float <– The extend of the Gabor wavelets
- transform()¶
- transform(input, output) -> None
- transform(input) -> output
This function transforms the given input image to the output trafo image
The input image must be of two dimensions and might be of any supported type: uint8, float or complex, whereas the output needs to be of 3 dimensions with complex type and of shape (number_of_wavelets, input.shape[0], input.shape[1]). The transform is defined as:
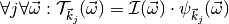
Both the input image and the output are expected to be in spatial domain, so don’t perform an FFT on the input image before calling this function.
Note
The function __call__() is a synonym for this function.
Parameters:
input : array_like (2D)
The image in spatial domain that should be transformedoutput : array_like (complex, 3D)
The transformed image in spatial domain that should contain the transformed image; must have shape (number_of_wavelets, input.shape[0], input.shape[1])Returns:
output : array_like (complex, 3D)
The transformed image in spatial domain that will contain the transformed image; will have shape (number_of_wavelets, input.shape[0], input.shape[1])
- wavelet_frequencies¶
[(float, float), ...] <– The central frequencies of the Gabor wavelets, in the same order as in wavelets
- wavelets¶
[Wavelet] <– The list of Gabor wavelets used in this transform
Note
The wavelets will be generated either by a call to generate_wavelets() or by a call to transform(). Before one of these functions is called, no wavelet will be generated.
- class bob.ip.gabor.Wavelet¶
Bases: object
A class that represents a Gabor wavelet in frequency domain
The implementation is according to [Guenther2011], where the whole procedure is explained in more detail.
Note
In this class, all input and output images are considered to be in frequency domain.
Constructor Documentation:
bob.ip.gabor.Wavelet (resolution, frequency, [sigma], [power_of_k], [dc_free], [epsilon])
Creates a Gabor wavelet in frequency domain for the given parametrization
The Gabor wavelet
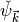 is created in
frequency domain as a Gaussian that is shifted from the origin of
the frequency domain:
is created in
frequency domain as a Gaussian that is shifted from the origin of
the frequency domain: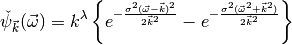
Parameters:
resolution : (int, int)
The resolution (height, width) of the Gabor wavelet; this must be the same resolution as the image that the Gabor wavelet is applied on laterfrequency : (float, float)
The location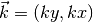 of the Gabor wavelet in
frequency domain; the values should be limited between
of the Gabor wavelet in
frequency domain; the values should be limited between
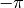 and
and 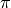
sigma : float
[default: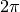 ] The spatial resolution
] The spatial resolution 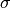 of the Gabor wavelet
of the Gabor waveletpower_of_k : float
[default: 0] The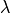 factor to regularize the Gabor
wavelet prefactor to generate comparable results for images,
see Appendix C of [Guenther2011]
factor to regularize the Gabor
wavelet prefactor to generate comparable results for images,
see Appendix C of [Guenther2011]dc_free : bool
[default: True] Should the Gabor wavelet be without DC factor (i.e. should the integral under the wavelet in spatial domain vanish)?epsilon : float
[default: 1e-10] For speed reasons: all wavelet pixels in frequency domain with an absolute value below this should be considered as 0Class Members:
- transform()¶
- transform(input, output) -> None
- transform(input) -> output
This function transforms the given input image to the output image
Both images are considered to be in frequency domain and need to have the same resolution and to be of complex type. The resolution must be the same as the one defined in the constructor. The transform is defined as:
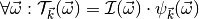
Note
The function __call__() is a synonym for this function.
Parameters:
input : array_like (complex, 2D)
The image in frequency domain that should be transformedoutput : array_like (complex, 2D)
The image in frequency domain that should contain the transformed image; must have the same size as inputReturns:
output : array_like (complex, 2D)
The image in frequency domain that will contain the transformed image; will have the same size as input
- wavelet¶
2D-array complex <– The image representation of the Gabor wavelet in frequency domain
The image representation is generated on the fly (since the original data format is different), the data format is float. To obtain the image representation in spatial domain, please perform a bob.sp.ifft() on the returned image.
- bob.ip.gabor.load_jets(hdf5) → jets¶
Loads a list of Gabor jets from the given HDF5 file, which needs to be open for reading.
Parameters:
- hdf5 : bob.io.base.HDF5File
- An HDF5 file open for reading
Returns:
- jets : [bob.ip.gabor.Jet]
- The list of Gabor jets read from file
- bob.ip.gabor.save_jets(jets, hdf5) → None¶
Saves the given list of Gabor jets to the given HDF5 file, which needs to be open for writing.
Parameters:
- hdf5 : bob.io.base.HDF5File
- An HDF5 file open for writing
- jets : [bob.ip.gabor.Jet]
- The list of Gabor jets to write to file