Presentation Attacks¶
This section contains information about the presentation attack dataset. For information about the biometric recognition dataset, refer to Biometric Recognition.
Data¶
To create effective presentation attacks for the VERA Fingervein Database, images from the dataset were printed on high-quality (200 grams-per-square-meter - GSM) white paper using a laser printer (toner can absorb to near-infrared light used in fingervein sensors), and presented to the sensor. More information and details can be found on Section 2.2 of the original publication [TVM14].
All presentation attacks were recorded using the same open finger vein sensor used to record the Biometric Recognition counterpart (see Biometric Recognition). Images are stored in PNG format, with a size of 250x665 pixels (height, width). Files are named in a matching convention to their counterparts in the biometric recognition. Size of the files is around 80 kbytes per sample.
All bonafide samples corresponds to unaltered originals from the VERA Fingervein Database.
Images in the full folder are stored in PNG format, with a size of 250x665
pixels (height, width). Size of the files is around 80 kbytes per sample.
Here are examples of presentation-attack (pa) samples from the full
folder inside the database, for subject 029-M:
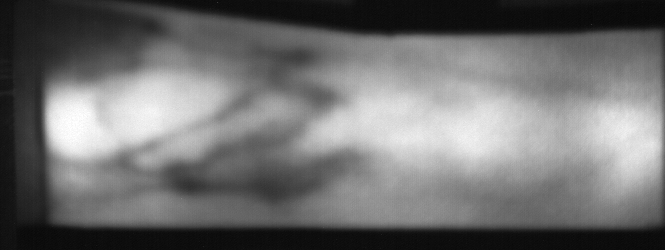
Fig. 9 Image from subject 0029 (male). This image corresponds to the first
trial for the left index finger.¶
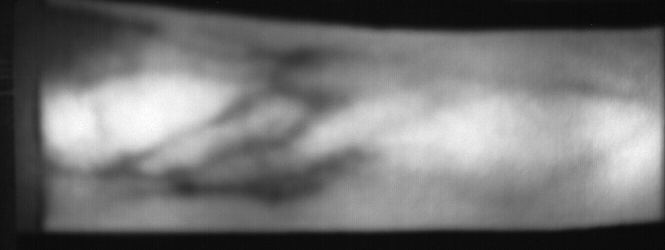
Fig. 10 Image from subject 0029 (male). This image corresponds to the second
trial for the left index finger.¶
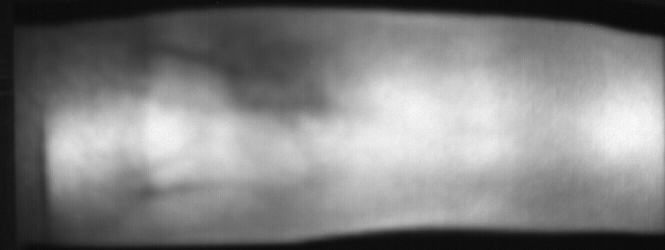
Fig. 11 Image from subject 0029 (male). This image corresponds to the first
trial for the right index finger.¶
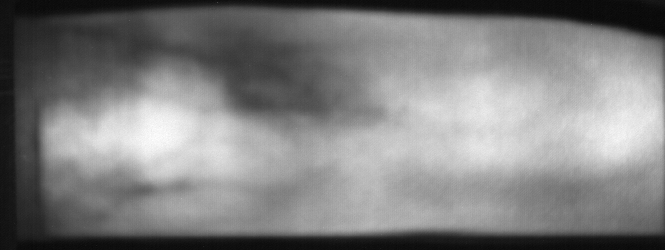
Fig. 12 Image from subject 0029 (male). This image corresponds to the second
trial for the right index finger.¶
Images in the cropped folder are stored in PNG format, with a size of
150x565 pixels (height, width). Size of the files is around 40 kbytes per
sample.
Here are examples of presentation-attack (pa) samples from the cropped
folder inside the database, for subject 029-M:

Fig. 13 Image from subject 0029 (male). This image corresponds to the first
trial for the left index finger. This version contains only the pre-cropped
region-of-interest.¶

Fig. 14 Image from subject 0029 (male). This image corresponds to the second
trial for the left index finger. This version contains only the pre-cropped
region-of-interest.¶

Fig. 15 Image from subject 0029 (male). This image corresponds to the first
trial for the right index finger. This version contains only the pre-cropped
region-of-interest.¶

Fig. 16 Image from subject 0029 (male). This image corresponds to the second
trial for the right index finger. This version contains only the pre-cropped
region-of-interest.¶
Protocols¶
There are 2 types of protocols available in this dataset:
Vulnerability Analysis: protocols for testing the vulnerability of biometric systems
Presentation Attack Detection: protocols for testing the efficiency of binary PA detectors
Vulnerability Analysis (va)¶
The first set of PA-related protocols available in this package allow the analysis of the vulnerability of established biometric recognition baselines when exposed to presentation attacks. For such purposes, the following sets of protocols exist in this package:
“Nom” and “Cropped-Nom”
“Fifty” and “Cropped-Fifty”
“B” and “Cropped-B”
“Full” and “Cropped-Full”
These protocols are matches for the biometric recognition protocols described
in Biometric Recognition, but with probes replaced by presentation
attacks only. Data for presentation attacks come from the subfolder of the
dataset named pa. Data for bona fide presentations come from the bf
folder as for biometric recognition. Vulnerability analysis can, currently,
only be executed using either full or cropped images.
This setup allows for testing the vulnerability of biometric systems. Notice that, unlike the biometric recognition protocols, presentation attack probes are only valid for the identity being spoofed. The number of probes per model is therefore reduced.
Presentation Attack Detection (pad)¶
Protocols in this category allow for training and evaluating binary-decision making counter-measures to Presentation Attacks. The available data comprised of bonafide and presentation attacks are split into 3 sub-groups:
Training data (“train”), to be used for training your detector;
Development data (“dev”), to be used for threshold estimation and fine-tunning;
Test data (“test”), with which to report error figures;
Clients that appear in one of the data sets (train, devel or test) do not appear in any other set.
Protocol “full”¶
In this protocol, the full image as captured from the sensor is available to the user. Here is a summary:
Training set: 30 subjects (identifiers from 1 to 31 inclusive). There are 240 samples on this set.
Development set: 30 subjects (identifiers from 32 to 72 inclusive). There are 240 samples on this set.
Test set: 50 subjects (identifiers from 73 to 124 inclusive). There are 400 samples on this set.
Protocol “cropped”¶
In this protocol, only a pre-cropped image of size 150x565 pixels (height, width) is provided to the user, that can skip region-of-interest detection on the processing toolchain. The objective is to test user algorithms don’t rely on information outside of the finger area for presentation attack detection. The subject separation is the same as for protocol “full”.